Model Inference¶
The inference pipeline generates predictions using trained MLflow models with explicit parameter requirements.
How It Works¶
The predict_model.py module follows a straightforward workflow:
def predict_model(
model_uri: Optional[str] = None,
model_type: Optional[str] = None,
input_path: Optional[str] = None,
output_path: Optional[str] = None
) -> pd.DataFrame:
"""Generate predictions from MLflow model and save to CSV.
Complete pipeline: validate inputs, load model, prepare data,
predict probabilities (with fallback), save results.
"""
config = load_config()
# Setup MLflow - Connect to tracking server
_setup_mlflow(config)
# Validate Parameters - Check all required params
model_uri = _validate_model_uri(model_uri)
input_path, output_path = _validate_paths(input_path, output_path)
# Load Model - Use algorithm-specific MLflow flavors
model = _load_model(model_uri, model_type, config)
# Process Data - Load and prepare prediction data
input_data = pd.read_csv(input_path)
prediction_data, ids, id_col = _prepare_prediction_data(input_data, config, model)
# Generate Predictions - Try probabilities, fallback to predictions
try:
probabilities = model.predict_proba(prediction_data)[:, 1]
predictions = probabilities.round(3)
except AttributeError:
predictions = model.predict(prediction_data)
# Save Output - Create and save Kaggle-compatible CSV
predictions_df = _create_predictions_dataframe(predictions, ids, id_col)
_save_predictions(predictions_df, output_path)
return predictions_df
The pipeline uses explicit validation at each step, failing fast with clear error messages if any requirements are not met.
Usage¶
Command Line¶
# Direct Python execution (Example selecting model and version)
python -m src.models.predict_model \
--model-uri models:/bank-client-subscription-classifier-xgboost/10 \
--model-type xgboost \
--input-path data/processed/test_processed.csv \
--output-path data/predictions/xgboost_predictions.csv
# MLflow entry point (Exmample selecting run directly)
mlflow run . -e predict \
-P model_uri=runs:/f2c64e293c9246fa904dd6f66bce8c9f/model \
-P model_type=xgboost \
-P input_path=data/processed/test_processed.csv \
-P output_path=data/predictions/xgboost_submission.csv
Programmatic Usage¶
from src.models.predict_model import predict_model
predictions_df = predict_model(
model_uri="models:/BankSubscriptionClassifier-xgboost/1",
model_type="xgboost",
input_path="data/processed/test_processed.csv",
output_path="data/predictions/final_submission.csv"
)
Parameters¶
All parameters are required:
model_uri: MLflow model URI (e.g.,models:/model-name/version)model_type: Algorithm type -lightgbm,xgboost, orcatboostinput_path: Path to input CSV fileoutput_path: Path to save predictions CSV file
Output Format¶
Generates Kaggle-compatible CSV files:
- ID column: Preserves test data IDs
- Target column: Named 'y' with probability values (0-1)
- Precision: Rounded to 3 decimal places
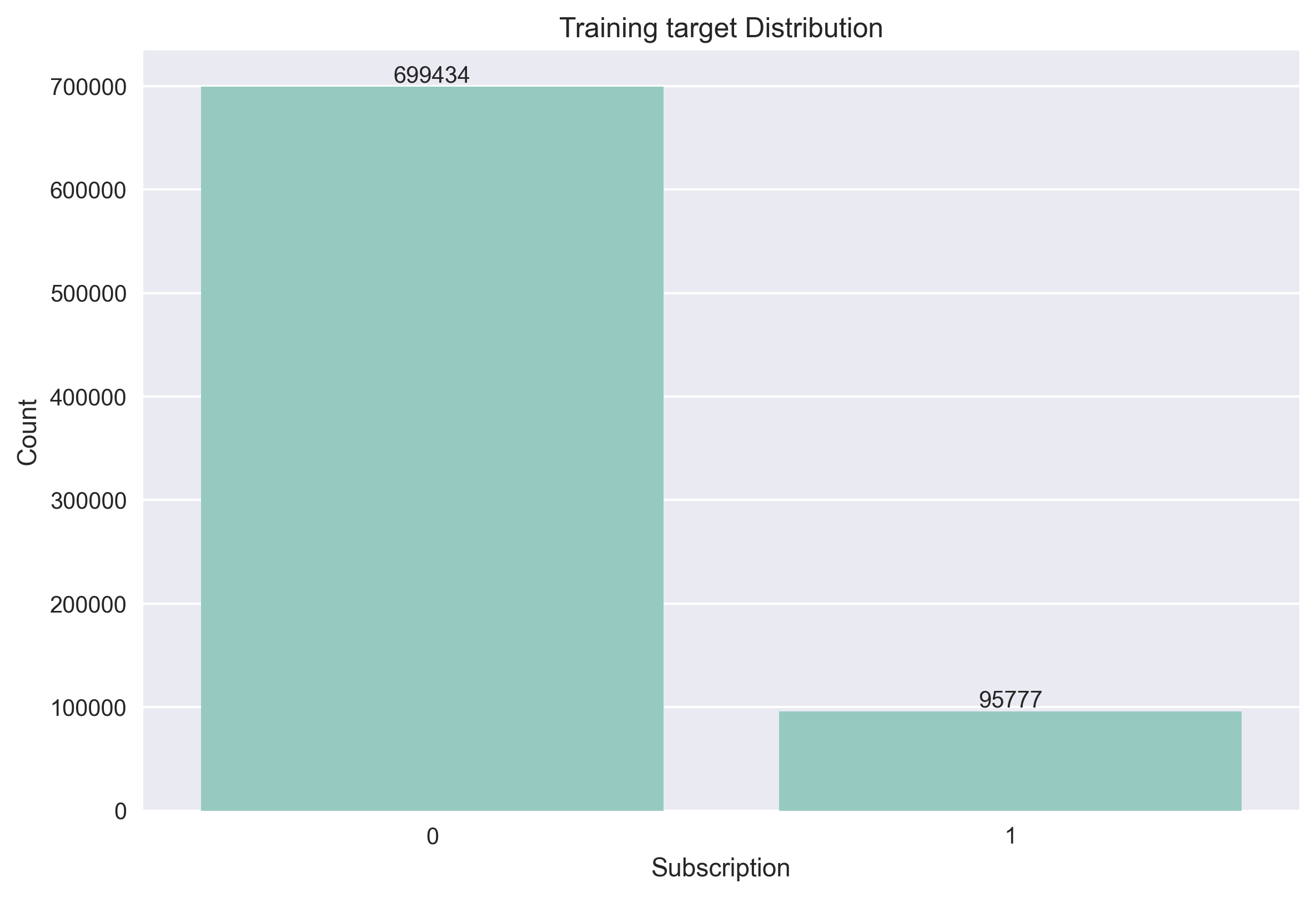
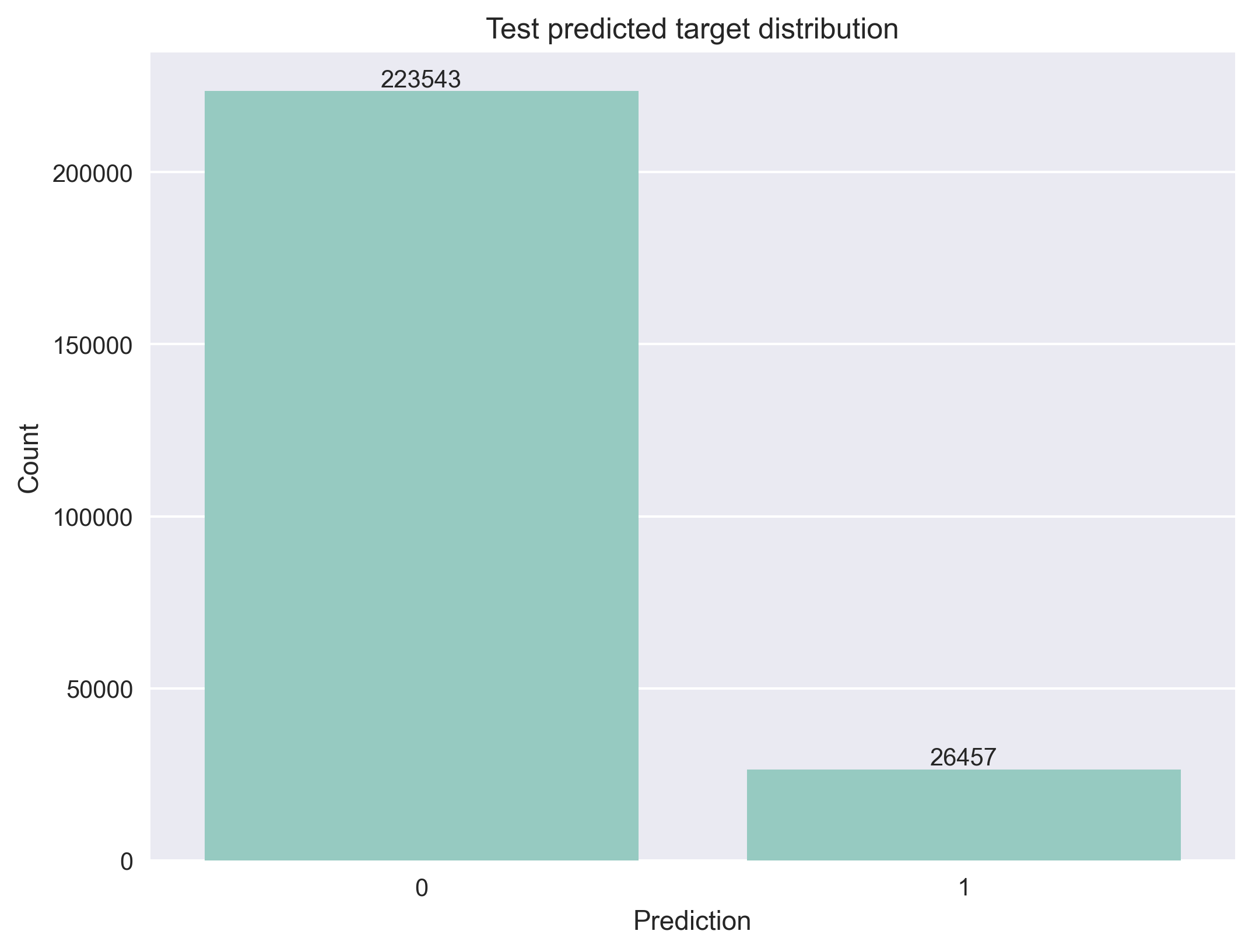
Distribution Analysis¶
A validation step in model inference is comparing the prediction distribution against the training target distribution. This analysis helps detect potential model issues, particularly in imbalanced datasets where models might predict a single class for all samples.
Training vs Predictions Distribution Comparison¶
The distribution comparison shows that the model maintains similar class proportions between training and test predictions, this indicates that the model isn't defaulting to predicting only the majority class and maintains decision boundaries learned during training